
Pharmacy Services
Buy from your local pharmacy
Nearby Locations
What is atopic dermatitis, how is it manifested and how is it treated?
One of the most common skin conditions, which is particularly common in young children but also affects adults, is atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis. What is atopic dermatitis? What are the causes of this skin disease? How does atopic eczema manifest itself and how is it treated?
About atopic eczema
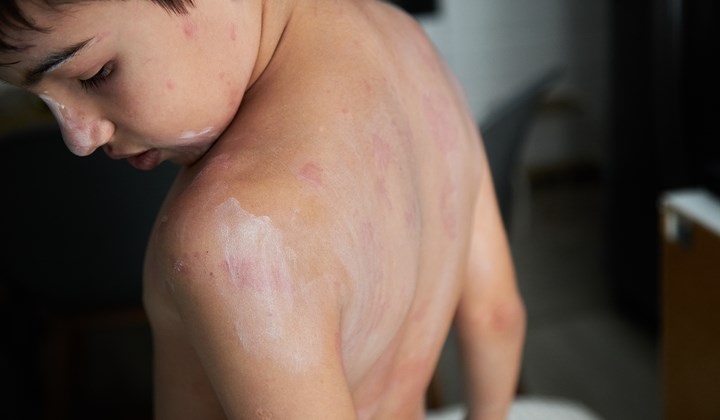
Right at the outset, let's clarify what atopic eczema is. Atopic eczema is a chronic skin disease that affects up to 30% of children and up to 10% of adults during their lifetime, and it affects women as often as men. Atopic eczema is classified as an episodic disease and alternates between periods of remissions and periods of flare-ups that are associated with severe symptoms. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious, despite the common belief.
Experts divide atopic eczema into three forms, namely infantile, child, and adult. In addition, there is mild atopic dermatitis and severe atopic dermatitis. The symptoms and localization of atopic dermatitis vary based on which form and how serious it is.
What are the symptoms of atopic dermatitis and what does it look like?
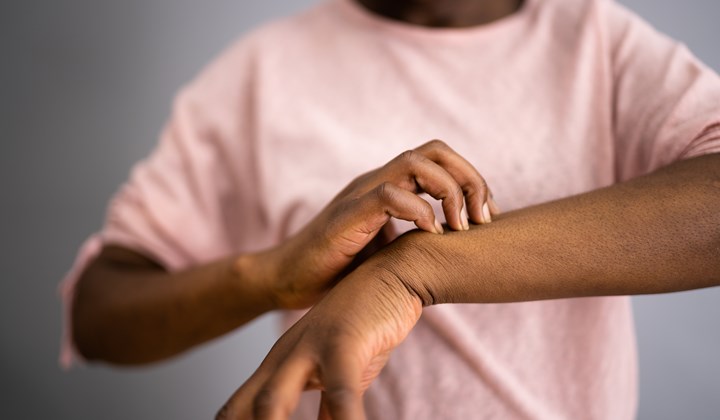
How does atopic eczema manifest itself and how do you know if you struggle with namely this skin disease? The main and most common symptom is the severe itching of the skin, which forces you to scratch the affected area constantly. Scratching the itchy area may bring momentary relief, but at the same time it significantly worsens the ongoing inflammation, so you should avoid it.
Other symptoms of atopic dermatitis include rash, redness and swelling of the skin, and small pimples that may become wet. These symptoms occur in the acute phase of eczema, or the flare-up phase. During the remission, the skin is dry, tight, slightly itchy, and scaly.
On which parts of the body is atopic eczema most common?
In infants and toddlers, atopic dermatitis usually first appears on the face and can then spread to the trunk and limbs. In older children, atopic dermatitis usually occurs at the back of the knee or elbow, on the hands, feet, and neck. In adults, atopic dermatitis most commonly affects the face, neck, upper chest, shoulders, and arms, and can also occur in the hair.
What causes atopic dermatitis?
What are the causes of atopic eczema? A number of factors influence the development of this disease, be it genetic predisposition, environmental influences or skin barrier defects. For example, stress, hormonal changes, allergens, changes in diet, contact with pets, or cold and heat can aggravate the symptoms of atopic eczema.
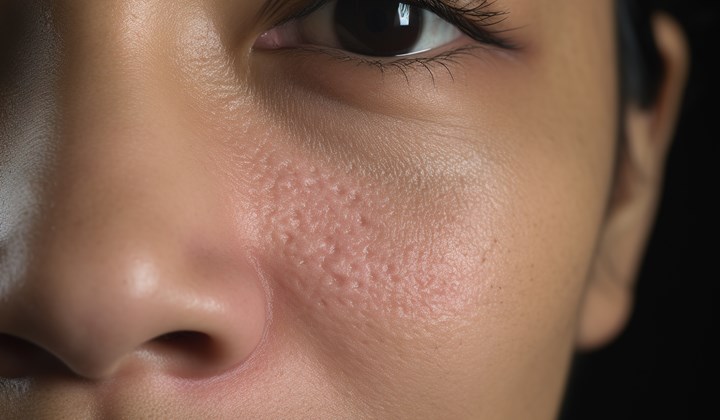

Atopic dermatitis: treatment
If you struggle with atopic eczema, then you are probably most interested in how to get rid of it. Unfortunately, there is no cure for atopic eczema, but there are a number of treatments and medications that relieve symptoms and help prevent further flare-ups. The aim of treating atopic eczema is therefore to bring the disease under control.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis depends on how severe the symptoms are. Your doctor may prescribe painkillers, antihistamines to help relieve itching, or topical corticosteroids, which also reduce inflammation and itching.
Applying emollient creams and ointments
In addition to taking the medication prescribed by your doctor, daily skin care is very important when treating atopic eczema. There are a number of special creams and shampoos for atopic dermatitis on the market that you should use regularly. These products, in the form of ointments and creams, are known as emollients and, thanks to their composition, they relieve the dryness of the skin and itching. In addition, they strengthen the skin barrier and regulate the skin microbiota.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/atopic-dermatitis/what-is-atopic-dermatitis
- https://www.healthline.com/health/eczema#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
- https://euc.cz/clanky-a-novinky/clanky/atopicky-ekzem-priciny-priznaky-a-lecba/
- https://www.benu.cz/atopicky-ekzem-1539073950
- https://www.bioderma-cz.com/vase-pokozka/sucha-az-atopicka-pokozka/podrazdena-svediva-atopicka-pokozka/jak-rozlisit-mezi-ruznymi-typy-ekzemu
- https://www.drmax.cz/clanky/atopicky-ekzem-priciny-priznaky-a-lecba


